Skin cancer is a prevalent form of cancer that develops in the skin’s cells. It occurs when the skin’s cells undergo abnormal changes, usually triggered by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. It is highly treatable when detected early, making it crucial to be aware of its causes, types, and prevention strategies.
Causes
Let’s discuss some major causes of skin cancer:
1. UV Radiation:
Prolonged exposure to UV radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds is the primary cause of skin cancer. UV rays damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can result in cancer.
2. Fair Skin:
People with fair color, light hair, and light-colored eyes are more susceptible to skin cancer, as they have less melanin, a pigment that provides some protection against UV radiation.
3. Family History:
A family history of skin cancer increases your risk. Firm genetic factors can make individuals more disposed to developing the disease.
Types
There are three primary types of skin cancer, each with distinct characteristics:
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC):
BCC is the most common type of skin cancer. It usually appears as a pearly bump or a sore that doesn’t heal. BCC rarely metastasizes but can cause disfigurement if left untreated.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC):
SCC typically manifests as a scaly, red patch or a firm, raised bump with a crusted surface. It can metastasize if not treated early but is generally less aggressive than melanoma.
3. Melanoma:
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. It often appears as an irregularly shaped mole or spot with uneven coloration and a border that may be jagged or blurry. Early detection is critical, as melanoma can spread rapidly.
Risk Factors
Let’s delve deeper into some important aspects of skin cancer:
While UV radiation is the primary cause of skin cancer, several risk factors can increase your susceptibility:
1. Sun Exposure:
Spending excessive time outdoors, especially without protection, increases the risk of skin cancer.
2. History of Sunburn:
A history of severe sunburns, especially during childhood, can elevate your risk.
3. Moles:
Having many moles or atypical moles (dysplastic nevi) can increase the likelihood of developing melanoma.
4. Weakened Immune System:
A weakened immune system due to diseases like HIV or medications like immunosuppressants can raise the risk of skin cancer.
5. Age:
While skin cancer can occur at any age, it is more common in older individuals due to accumulated UV exposure over time.
6. Exposure to Radiation:
Previous radiation therapy can increase the risk of developing non-melanoma skin cancers in the treated area.
Related: Deadly Symbols Of Skin Cancer You Must Spot Early
Initial Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection of skin cancer is crucial for successful treatment. Dermatologists use various methods to diagnose skin cancer, including:
1. Visual Inspection:
Dermatologists examine the skin’s surface, looking for irregularities in moles, freckles, and other skin marks.
2. Dermoscopy:
This technique uses a handheld device to magnify skin structures, aiding in the diagnosis of melanoma.
3. Skin Biopsy:
If a suspicious lesion is found, a small tissue sample (biopsy) is taken for examination under a microscope to determine if it is cancerous.
4. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy:
For melanoma, this procedure helps determine if cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer. Common treatment options include:
1. Surgery:
The most common treatment, it involves the removal of the cancerous tissue and, if necessary, some surrounding healthy tissue.
2. Radiation Therapy:
It may be used in some cases, particularly for basal cell or squamous cell carcinoma.
3. Mohs Surgery:
A precise surgical technique often used for treating skin cancers on the face, where preservation of healthy tissue is critical.
4. Immunotherapy:
These drugs boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
5. Targeted Therapy:
These medications target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
6. Chemotherapy:
Although less common, chemotherapy may be used in some advanced cases.
Skin Cancer Survival Rates
Survival rates are generally high, especially when diagnosed and treated early. For melanoma, the survival rate is approximately 95% for localized cases but drops significantly for advanced stages. For non-melanoma skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, the survival rate is even higher.
Prevention Strategies
1. Sun Protection:
Reduce your risk of skin cancer by wearing sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher, protective clothing (such as long sleeves and wide-brimmed hats), and sunglasses when outdoors. Try to find shade during peak sun hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
2. Self-Examination:
Regularly examine your skin for any unusual changes, such as new moles, changes in the size or color of existing moles, or sores that don’t heal. Refer a dermatologist if you notice any abnormalities.
3. Avoid Tanning Beds:
Tanning beds emit UV radiation that significantly increases the risk of it. Avoid their use altogether.
4. Routine Checkups:
Schedule regular examination with a dermatologist, especially if you have a family history of cancer or other risk factors.
5. Know Your ABCDEs:
Use the ABCDE rule to identify potential melanomas:
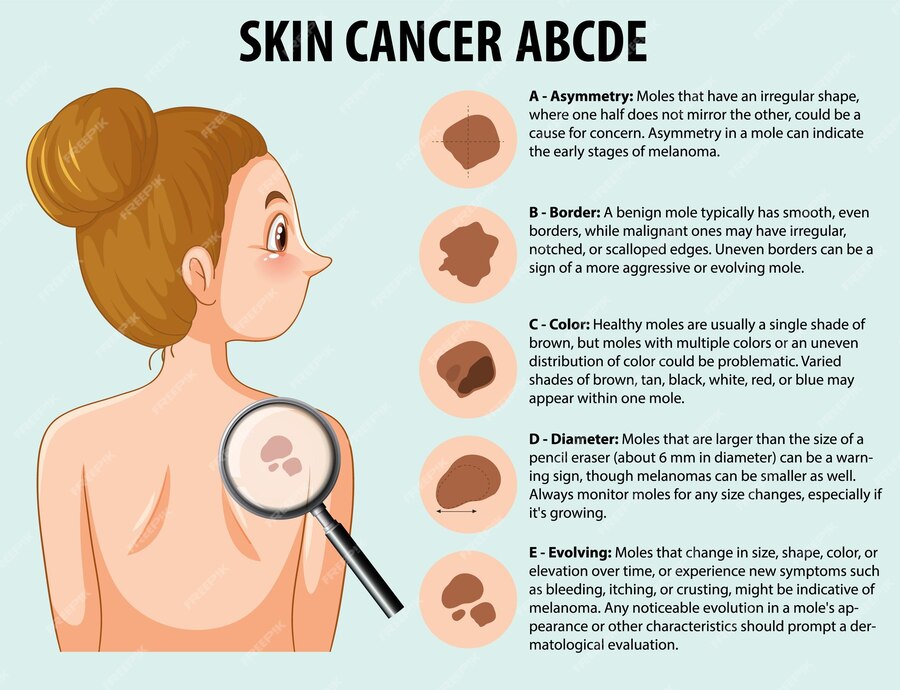
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t bout the other.
- Border: The edges are uneven, blurred, or poorly defined.
- Color: The mole has varying shades of color or is not uniform.
- Diameter: Melanomas are often larger than 6 millimeters (the size of a pencil eraser).
- Evolution: Look for any changes in size, shape, color, or symptoms over time.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a widespread and largely preventable disease. Understanding the causes, risk factors, early detection methods, and treatment options is crucial for protecting your skin and overall health. Practicing sun safety, regular self-examinations, and promptly consulting a dermatologist if you notice any suspicious changes in your skin are key steps in reducing your risk of skin cancer and ensuring early intervention if necessary. Remember that prevention and early detection can make a significant difference in the outcome of skin cancer cases. Stay informed and take action to safeguard your skin’s health.